Hyper Parameter Optimization (HPO) with DeepHyper
An overview of hyperparameter optimization can be found here. DeepHyper [1] uses Bayesian Optimization with parallel procesing to determine optimal hyperparameters using the validation loss. More information on DeepHyper can be found here.
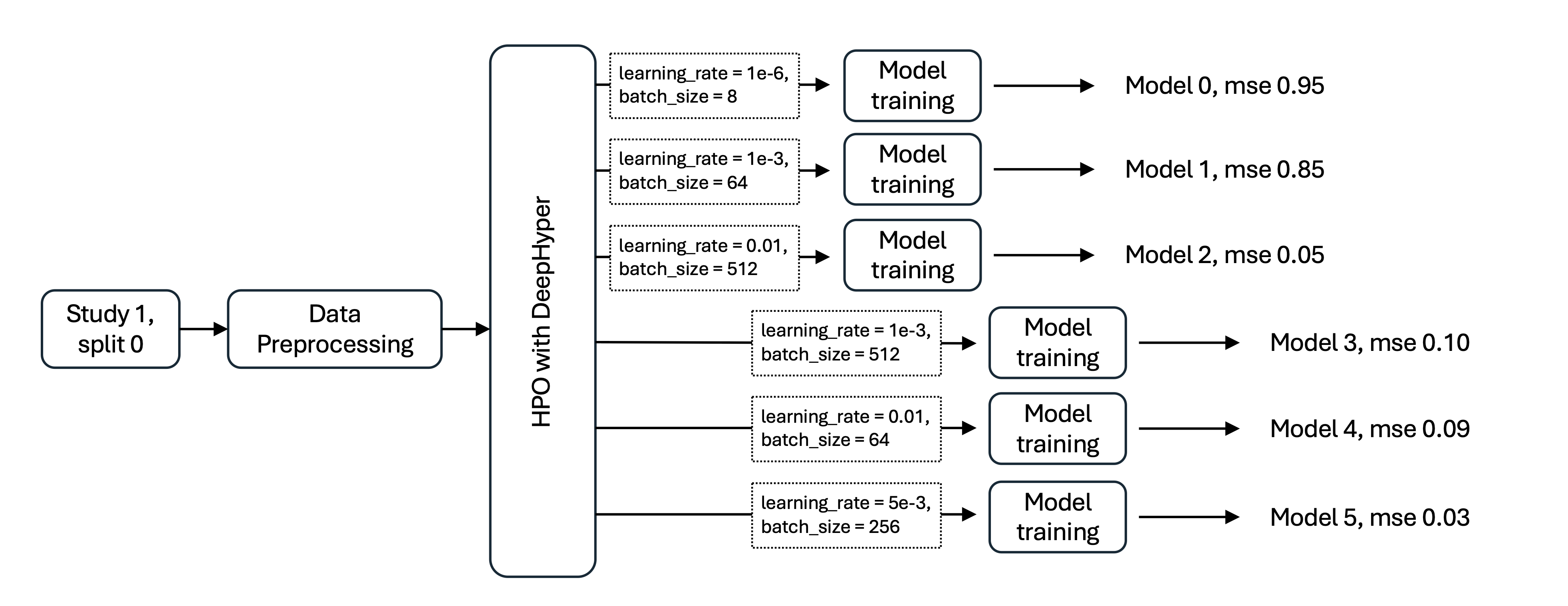
HPO workflow using DeepHyper
Run HPO using DeepHyper with conda
The DeepHyper HPO workflow uses two different conda environments. The DeepHyper environment is used to run the entire workflow, and the model-specific environment is used during each subprocess.
1. Install conda environment for the curated model
Install model, IMPROVE, and datasets:
cd <WORKING_DIR>
git clone https://github.com/JDACS4C-IMPROVE/<MODEL>
cd <MODEL>
source setup_improve.sh
Install model environment (get the name of the yml file from model repo readme):
The workflow will need to know the ./<MODEL_ENV_NAME>/.
conda env create -f <MODEL_ENV>.yml -p ./<MODEL_ENV_NAME>/
2. Perform preprocessing
Run the preprocess script.
The workflow will need to know the <PATH/TO/PREPROCESSED/DATA>.
cd PathDSP
conda activate ./<MODEL_ENV_NAME>/
python <MODEL_NAME>_preprocess_improve.py --input_dir ./csa_data/raw_data --output_dir <PATH/TO/PREPROCESSED/DATA>
conda deactivate
3. Install conda environment for DeepHyper
module load openmpi
conda create -n dh python=3.9 -y
conda activate dh
conda install gxx_linux-64 gcc_linux-64
pip install "deephyper[default]"
pip install mpi4py
Important
If openmpi is installed on your system, you may not need the line module load openmpi. The module may have another name on your system (e.g. openmpi/4.1.4/CUDA-11.4/gcc-8.5.0 on NIH’s Biowulf).
4. Modify configuration file
hpo_deephyper_params.ini is an example configuration file for this workflow.
You will need to change the following parameters for your model:
model_scripts_dirshould be set to the path to the model directory containing the model scripts (from step 1).input_dirshould be set to the location of the preprocessed data (above). We highly recommend that the name of this directory includes the source and split (e.g. ./ml_data/CCLE-CCLE/split_0). You can provide a complete or relative path, or the name of the directory if it is in model_scripts_dir.model_nameshould be set to your model name (this should have the same capitalization pattern as your model scripts, e.g. deepttc for deepttc_preprocess_improve.py, etc).model_environmentshould be set to the location of the model environment (from step 1). You can provide a complete or relative path, or the name of the directory if it is inmodel_scripts_dir.output_dirshould be set to path you would like the output to be saved to. We highly recommend that the name of this directory includes the source and split (e.g. ./deephyper/CCLE/split_0)epochsshould be set to the maximum number of epochs to train for.max_evalsshould be set to the maximum number of evaluations to check for before launching additional training runs.interactive_sessionshould be set to True to run on Lambda. Other implementations have not yet been tested.hyperparameter_filecan be set to an alternate .json file containing hyperparameters. You can provide a complete or relative path, or the name of the directory if it is inmodel_scripts_dir. See below (step 5) for how to change hyperparameters.num_gpus_per_nodeis set to 2 by default, but can be changed if you have more GPUs per node.
5. Modify hyperparameters file
The file hpo_deephyper_hyperparameters.json contains dictionaries for the hyperparameters.
The default settings are as follows:
Hyperparameter |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Default |
batch_size |
8 |
512 |
64 |
learning_rate |
1e-6 |
0.01 |
0.001 |
You can add more hyperparameters to test by adding additional dictionaries to this list. An example of an alternate hyperparameters file is hpo_deephyper_hyperparameters_alternate.json. Insure that the name is a valid parameter for the model you are using. Categorical hyperparameters can be added as follows:
{
"name": "early_stopping",
"type": "categorical",
"choices": [true, false],
"default": false
}
Note that boolean values must be lowercase in JSON files.
6. Perform HPO
Navigate to the DeepHyper directory
cd <WORKING_DIR>/IMPROVE/workflows/deephyper_hpo
If necesssary (i.e not proceeding directly from above steps), activate environment:
module load openmpi
conda activate dh
export PYTHONPATH=../../../IMPROVE
Run HPO:
mpirun -np 10 python hpo_deephyper_subprocess.py
To run HPO with a different config file:
mpirun -np 10 python hpo_deephyper_subprocess.py --config <ALTERNATE_CONFIG_FILE>
Running large scale jobs with DeepHyper HPO workflow
Example job script for Argonne’s Polaris
#!/bin/bash -l
#PBS -l select=2:system=polaris
#PBS -l place=scatter
#PBS -l walltime=0:30:00
#PBS -q debug
#PBS -A IMPROVE_Aim1
#PBS -l filesystems=home:grand:eagle
module use /soft/modulefiles
module load nvhpc-mixed craype-accel-nvidia80
module load conda
conda activate
cd ${PBS_O_WORKDIR}
# MPI example w/ 4 MPI ranks per node spread evenly across cores
NNODES=`wc -l < $PBS_NODEFILE`
NRANKS_PER_NODE=4
NDEPTH=8
NTHREADS=1
NTOTRANKS=$(( NNODES * NRANKS_PER_NODE ))
echo "NUM_OF_NODES= ${NNODES} TOTAL_NUM_RANKS= ${NTOTRANKS} RANKS_PER_NODE= ${NRANKS_PER_NODE} THREADS_PER_RANK= ${NTHREADS}"
export PYTHONPATH=/lus/eagle/your/path/to/IMPROVE/
export MPICH_GPU_SUPPORT_ENABLED=1
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
mpirun -n ${NTOTRANKS} --ppn ${NRANKS_PER_NODE} --depth=${NDEPTH} --cpu-bind depth --env OMP_NUM_THREADS=${NTHREADS} python hpo_deephyper_subprocess.py
Example job script for NIH’s Biowulf
References
1. P. Balaprakash et al. “DeepHyper: Asynchronous Hyperparameter Search for Deep Neural Networks”, IEEE, 2018